有機化學/二烯烴
二烯烴指含有分子中含有兩個碳碳雙鍵的有機化合物。
二烯烴種類
[编辑]孤立二烯烴(Isolated Dienes)
[编辑]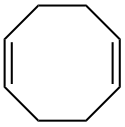
孤立二烯烴為兩個雙鍵相隔兩個以上單鍵的二烯烴。
孤立二烯烴的雙鍵距離太晚,一般不會有特殊的反應。可以視為比較大的烯烴來判斷反應。
累積二烯烴(Cumulated Dienes)
[编辑]
累積二烯烴為兩個雙鍵相鄰的二烯烴。最簡單的形式為丙二烯。
Cumulated dienes are typically less stable than other alkenes. The main reason for the instability is the fact that this sort of diene is a probable transition state for an alkyne's triple bond to move down the carbon chain towards the most stable position. As you may recall, rotation does not occur around any π-bond, which means that cumulated double bonds can lead to a less stable, higher energy compound being formed.
Typically, cumulated dienes are discussed only in advanced courses in organic chemistry, and so they will not be discussed in detail here. Beginning organic chemistry students should merely remember that cumulated dienes are 1) high energy and 2) most likely found as transition states.
共軛二烯烴(Conjugated Dienes)
[编辑]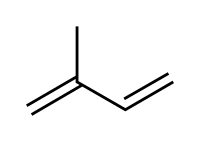
共軛二烯烴為兩個雙鍵中間恰有一個單鍵的二烯烴。
Conjugated dienes are dienes which have at least two double bonds separated by a single carbon-carbon bond, and for this reason conjugated dienes are observed to have a special stability due to the overlap of electron orbitals. The areas of concentration of negative charge (electron density) overlap across the three bonds (two double bonds and one single bond) forming what behaves essentially as a single, continuous π-bond across three carbon atoms. This delocalization of electron density stabilizes the molecule, resulting in the arrangement of lowest energy.
Atoms other than carbon which are capable of multiple bonds may also participate in conjugation. The heteroatoms most often associated with conjugation in dienes and other molecules are nitrogen and oxygen, but theoretically the majority of atoms in the Periodic Table of Elements could participate in conjugation chemistry. Most often, in organic molecules, heteroatoms participating in conjugation will be nitrogen atoms within a ring structure or a double-bonded oxygen attached to form a ketone or aldehyde.
Conjugation of double bonds is the largest part of what makes aromaticity relevant in organic chemistry, and conjugated double bonds have many other significant impacts on other types of dienes as well.
共軛
[编辑]雙鍵的共軛
[编辑]二烯烴特性與反應
[编辑]Common Reactions of Conjugated Dienes
[编辑]氫溴化
[编辑]狄耳士-阿德爾反應(Diels-Alder Reaction)
[编辑]狄耳士–阿德爾反應是一種環加成反應,共軛雙烯與取代烯烴(一般稱為親雙烯體)反應生成取代環己烯。
狄爾斯-阿爾德反應有如下規律:
1、區域選擇性:反應產物往往以“假鄰對位”產物為主。即若把六元環產物比作苯環,那麼環上官能團(假設有兩個官能團)之間的相互位置以鄰位(如1),或者對位為主(如3)。

2、立體選擇性:反應產物以“內型(即5)”為主,即反應主產物是經過“內型”過渡態得到的。

3、立體專一性:加熱條件下反應產物以“順旋”產物為唯一產物;光照條件下以“對旋”產物為唯一產物。
比如以下兩個熱反應中,產物7、8的相對立體構型都是唯一的,兩個烯烴原料原有的官能團A,B,C,D的順反立體化學關係,都在產物中得到忠實地翻譯。

